In various industries such as power plants and refineries, boilers play a significant role in producing steam and hot water. The proper operation of boilers is directly dependent on the quality of the feedwater, as water containing salts, minerals, and dissolved gases can cause scaling, corrosion, and ultimately a reduction in boiler efficiency. As a result, boiler water treatment in industry is not only a basic necessity but also a guarantee for sustainable efficiency and reduced operational costs.
Boiler water treatment
Treatment is a process that prevents potential damage to the system by eliminating impurities from the incoming water to the boiler. Boiler water treatment includes various stages, each of which plays a vital role in guaranteeing the boiler’s health and improving its performance. This process leads to increased efficiency, reduced scaling, and prevention of corrosion in the boiler, which consequently lowers maintenance and repair costs while extending the life of the equipment.
Steps in boiler water treatment
Water treatment encompasses processes that help remove impurities, reduce hardness, and control the chemical properties of water to prevent corrosion, scaling, and damage to boilers. These steps include primary filtration, ion exchange softening, reverse osmosis mineral removal, dissolved gas elimination, and pH adjustment through chemical dosing, each of which is explained separately.
Primary filtration
In the first step of boiler water treatment, impurities and large particles, such as soil, which can damage the boiler system, are removed. Initial filtration includes various methods such as sand filters, carbon filters, and micron filters.
Sand filter: This method of filtration is widely used. In a sand filter, water flows through a sand bed. Suspended impurities are captured in the upper sand layers, and the filtered water exits from the bottom.
Carbon filter: This filtration is used to remove dissolved chemicals and organic substances in water. Activated carbon has the ability to adsorb chemicals, such as chlorine. Carbon filtration is very effective in eliminating odors and tastes from water.
Micron filter: Micron filtration is used to remove ultra-fine particles ranging from 1 to 100 microns. Its extremely small pores effectively capture tiny contaminants. This type of filter is used when high precision is required in boiler water treatment processes.


Water softening by ion exchange
The second step in boiler water treatment is ion exchange softening, which is used to remove calcium and magnesium ions, the main contributors to water hardness. In this process, a resin bed containing sodium or potassium ions is employed. When hard water flows through the resin bed, the calcium and magnesium ions in the water are exchanged with sodium or potassium ions on the resin. This process decreases water hardness and prevents scaling in the equipment.
Over time, the resin becomes saturated and needs to be washed with a brine solution to remove the calcium and magnesium ions, thereby regenerating the resin. The ion exchange method for water softening is commonly employed in industrial applications, improving equipment efficiency and extending its lifespan.


Mineral removal by reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis is a key step in boiler water treatment, designed to eliminate impurities and minerals from the water. After undergoing primary filtration, the water is directed into the reverse osmosis system. At this stage, it passes through a semi-permeable membrane that effectively removes minerals such as chloride, nitrate, sulfate, silicic acid, bicarbonate, and others, ensuring high-quality water for boiler operation. This membrane only allows water molecules to pass through, preventing the passage of ions and suspended particles. Reverse osmosis is used in various industries, including drinking water production and boiler water treatment.


Removal of dissolved gases in water
Another step in boiler water treatment is the removal of dissolved gases in water. The removal of dissolved gases can be achieved through two methods: the addition of chemicals and the use of a deaerator.
Adding chemicals
Using chemicals to remove oxygen from boiler water is a highly effective method for preventing corrosion and protecting equipment. Chemicals like sodium sulfite (Na2SO3) and hydrazine (N₂H₄) are added to the water, where they react with oxygen, converting it into harmless compounds and safeguarding the system. Sodium sulfite rapidly converts oxygen into sulfate, while hydrazine can be converted into water and acts as a corrosion inhibitor.
Using deaerator
A deaerator is a crucial device in the boiler room of steam boilers, responsible for removing dissolved gases, especially oxygen and carbon dioxide, from the boiler feedwater. It operates by introducing a portion of the steam generated by the boiler from the bottom into the deaerator, raising the water temperature. As the solubility of dissolved gases decreases with rising temperature, the steam facilitates the separation of dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide from the water, allowing them to exit through the deaerator’s vent.
Oxygen and carbon dioxide gases acidify boiler water. The acidification of the water accelerates corrosion in equipment, resulting in a reduced lifespan. Thus, removing these gases from the water with a deaerator helps significantly extend equipment life, enhance boiler efficiency, and lower maintenance costs.


pH regulation of water by chemical dosing
Chemical dosing refers to the process of adding chemicals to water in specific, controlled amounts to adjust its pH. The pH value measures the acidity or alkalinity of a substance. A lower pH indicates a higher CO2 content. To prevent corrosion, the water pH should typically be maintained above 9. The dosing system is designed to protect the boiler from the accumulation of insoluble substances in the water and from corrosion in various boiler components caused by the acidic pH. The pH of the water can be increased by adding alkaline substances, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and trisodium phosphate (Na₃PO₄).
Ensuring Boiler Water Quality
Proper boiler water quality management is essential for managing performance and maintenance of industrial boiler systems. Even with advanced treatment systems, the quality of the output water must be continuously monitored and controlled to prevent issues such as corrosion, scaling, and reduced efficiency.
The key parameters monitored in boiler water quality include water hardness, pH level, dissolved oxygen, dissolved carbon dioxide, and total dissolved solids (TDS). These factors are regularly measured using accurate laboratory tools or online monitoring systems, and their data serves as the basis for adjusting treatment processes and chemical injection.
For instance, maintaining the pH of the water within the appropriate range is essential to prevent corrosion. Also, high levels of TDS or water hardness can indicate a malfunction in the softener or chemical dosing system, and if left unaddressed, may lead to scale formation in the pipes.
Overall, accurate and continuous monitoring of boiler water quality not only protects the equipment, but also helps optimize energy use, reduce operating costs, and enhance system safety. A regular monitoring plan with proper data recording and analysis is essential to ensure the stable and reliable performance of the boiler in various industries.
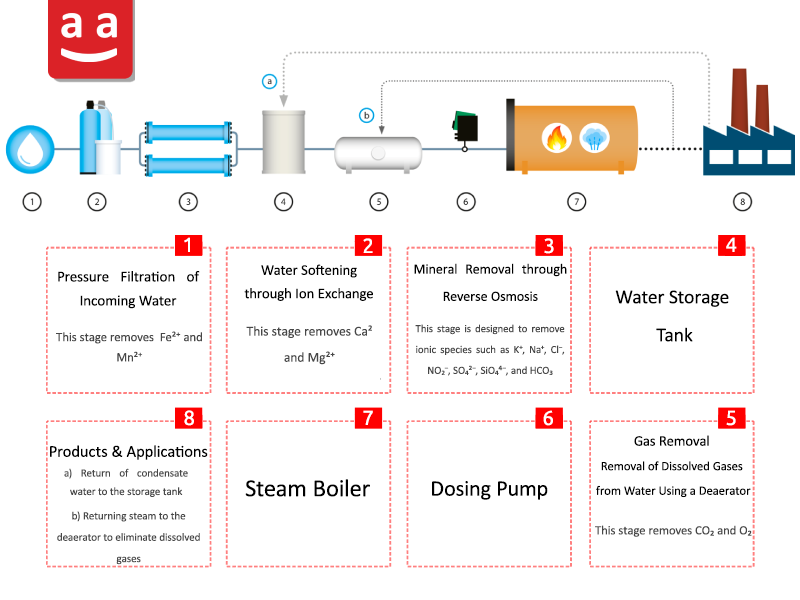

Operation of steam boiler water treatment
Untreated water (usually well water) initially enters the sand filtration system, where large particles such as soil and gravel are removed. Afterward, it enters the water softener. In the softener, resin beds containing sodium or potassium ions are used. The calcium and magnesium ions, which cause water hardness, are removed by these resin beds, and the “softened water” is then directed to the deaerator chamber. In addition to the softened water, the condensate water from the condensate chamber also enters the deaerator.
In the deaerator, a portion of the steam produced by the steam boiler enters from the bottom, increasing the water temperature. This causes dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide gases to separate from the water and exit through the deaerator’s vent. In the dosing system, alkaline substances such as sodium hydroxide are injected to raise the pH of the water inside the deaerator, making the water alkaline. The treated water is then pumped into the steam boiler through the feedwater pump.


Boiler water treatment: Protecting Equipment and Optimizing Industrial Processes
Boiler water treatment process plays a key role in preserving the optimal performance and increasing the lifespan of the boiler and related equipment. Boiler water treatment plays a crucial role in preventing significant damage to boiler components and improving overall system performance by effectively removing minerals and dissolved gases, regulating the water’s pH, and preventing corrosion and scaling. Reducing the need for frequent repairs and enhancing energy efficiency are additional benefits of boiler water treatment, leading to lower operational costs. By implementing a comprehensive water treatment system, both directly and indirectly, boiler efficiency improves, energy consumption decreases, and overall industry productivity increases, ensuring stable and cost-effective performance over the long term.





