From past to present, combustion and furnaces have been played a crucial role in society. The combustion process and industrial furnaces are critical in many industries, facilitating the production of essential goods, from food and beverages to advanced materials like metals and glass. In particular, furnaces are indispensable for processes that require high-temperature environments, such as ceramics production, metal production, glass melting, and casting in both metallic and non-metallic industries. Depending on their application, industrial furnaces are categorized by the type of fuel they consume, whether it’s gas, oil, or other energy sources, as well as their specific functions in various industrial sectors.
The effectiveness and efficiency of these furnaces largely depend on the design and operation of the burners they use. Industrial furnace burners must be carefully selected and installed based on the furnace load and the operating temperature required, often surpassing 400°C. As the heart of the furnace, these burners determine not only the energy output but also the environmental impact in terms of emissions like NOx (nitrogen oxides), which necessitates the use of efficient burner technologies and control methods to minimize pollution.
If you are interested in learning more about all types of industrial burners, the article “A Comprehensive Guide to Industrial Burners” provides further details.
What is an Industrial Furnace Burner?
Burners are widely used in different industries to facilitate and regulate combustion. Industrial furnace burners, in particular, are used to generate the heat needed for furnaces. By accurately combining various fuels—including natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, heavy fuel oil, or hybrid fuels—with air or oxygen, these burners create a stable and controllable flame, ensuring optimal heat distribution for diverse industrial applications.
As key components of industrial furnaces, burners are widely utilized in industries such as petrochemicals, steel, ceramics, cement, glass, and food production. Their designs vary based on application requirements, enabling them to produce extremely high temperatures. They are essential for processes like melting, firing, drying, heating, and heat treatment, which require high and controllable temperatures.


Operating Principles of Industrial Furnace Burners
In an industrial furnace burner, combustion takes place by mixing fuel with an oxidizer, such as air or pure oxygen. This process is carefully designed to generate a stable and high-efficiency flame, providing the required energy for various industrial applications.
Fuel and Oxidizer Supply
Initially, fuel (like natural gas or oil) and the oxidizer (air or pure oxygen) are introduced into the burner either separately or as a mixture. Burners are classified into two types based on where the fuel mixes with the air:
- Nozzle-mix: In this method, fuel and air are introduced separately into the burner and are mixed and ignited at the end of the combustion head.
- Premixed: In this method, fuel and air are completely mixed before entering the combustion head. The fuel-air mixture ignites in the combustion head, initiating the combustion process.
Flame Formation
Within the combustion head, the fuel ignites and forms a flame. The design of the furnace burner is configured to adjust the flame shape according to the type of furnace and the desired process.
Adjustment and Control
The flame, temperature, and flow rates of fuel and air are monitored and optimized by advanced control systems. These adjustments ensure that the burner operates with high efficiency under various conditions.
Enhancing Efficiency
At the final stage, some burners are fitted with extra equipment for energy recovery that use excess heat from the output to preheat air or fuel. These techniques help reduce fuel consumption and enhance thermal efficiency.
Applications of Industrial Furnace Burners
Industrial furnace burners are used in various industries, playing a critical role in improving the performance and efficiency of industrial processes. We will examine these applications more closely below:
Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical Industries
Furnace burners are crucial in the petrochemical sector, facilitating production and conversion processes. These burners are used for their ability to generate high temperatures and provide precise flame control to supply the heat required for chemical reactions and thermal processes. Some of their primary applications include:
Heat Supply in Cracking Furnaces: Used for breaking down heavy hydrocarbon molecules into lighter compounds such as ethylene, propylene, and other feedstocks for plastics and chemicals.
Distillation and Refining Units: Providing the necessary heat for evaporating the incoming crude oil in the distillation column to produce petrochemical products such as gasoline, oil, and feedstock materials.
Reforming Processes: Supplying heat for converting natural gas or hydrocarbons into syngas, which is used in the production of methanol, ammonia, and other chemical products.
Furnaces for Catalyst Reduction and Calcination: Providing the necessary temperature for activating or regenerating catalysts utilized in chemical reactions.
Steam Production: Generating high-pressure steam for use in industrial processes and providing thermal energy for petrochemical systems.
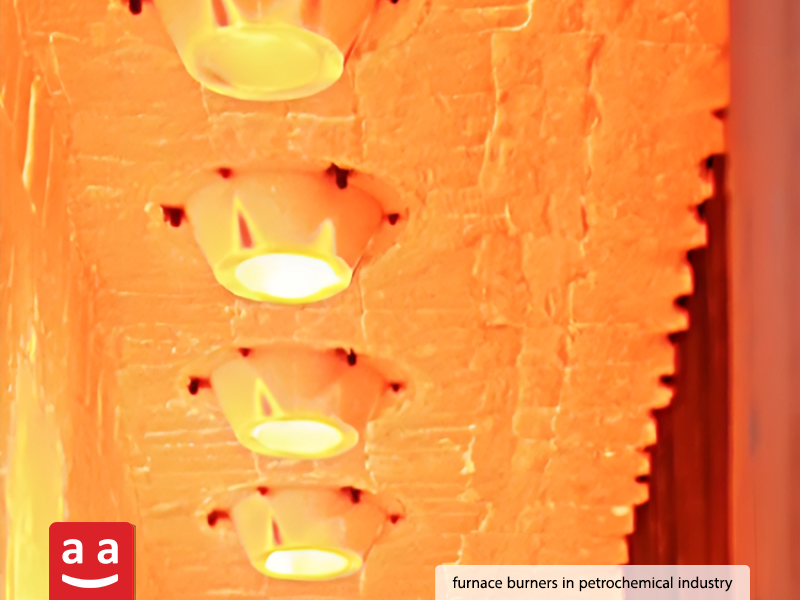


Steel and Metals
Furnace burner is used in the steel and metals industry for various processes that require high temperatures. In this sector, burners play a crucial role in determining the quality of metal products. The main applications include:
Metal Melting: Furnaces use burners to supply the heat required for melting processes. This heat is crucial for converting raw metal materials or scrap into molten metal.
Heat Treatment Operations: Burners are used in heat treatment furnaces for processes such as hardening, annealing, normalizing, and stress relieving. These processes enhance the mechanical and structural properties of metals.
Rolling Furnaces: Industrial burners are employed to heat billets and metal sheets prior to the rolling process. This heating lowers the resistance of the metal and eases the shaping procedure.
Refining and Reduction: In processes such as sponge iron production and direct reduction, burners are used to remove impurities and produce pure metals. These applications in reduction and refining furnaces help reduce costs and improve product quality.
Key Features of Furnace Burners in the Metals Industry
Furnace burners have a crucial impact on the efficiency and quality of thermal operations in the metals sector, including:
- High-temperature for melting and shaping
- Precise flame adjustment for sensitive processes
- Reduced fuel consumption and environmental pollution through advanced technologies
- Ability to operate in heavy industrial environments with high durability
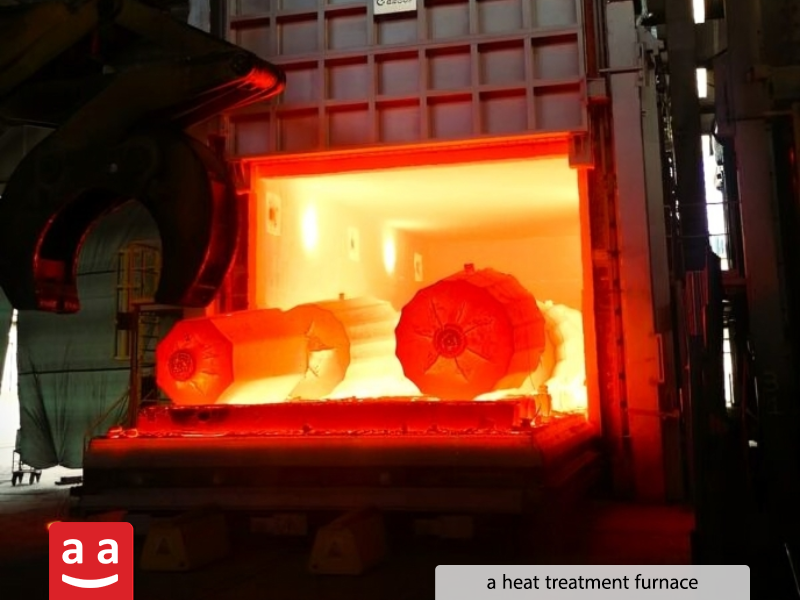


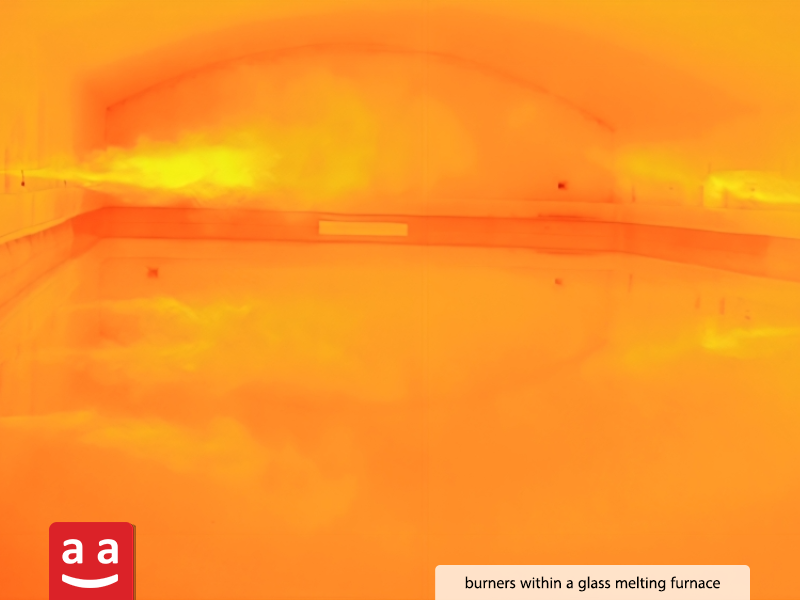
Glass and Ceramics
furnace burners are used in the glass and ceramics industries for sensitive processes requiring high temperatures. These burners improve product quality and enhance efficiency by generating adjustable and uniform flames. The main applications include:
Melting Raw Materials for Glass: Burners are used in melting furnaces to provide the necessary heat to transform raw materials (such as silica, sodium carbonate, and lime) into molten glass. High temperature and precise flame control are essential to ensure the clarity and quality of the glass.
Ceramic Firing: In ceramic firing furnaces, burners provide the necessary heat to harden and stabilize the structure of ceramic materials. This process involves creating a uniform temperature to prevent cracking and enhance the strength of the pieces.
Annealing Process: Burners play a role in the annealing phase by heating and reducing internal stresses in glass and ceramics. This process contributes to improving mechanical resistance and preventing the product from cracking.
Glazing and Surface Coating: In glazing applications, burners provide heat to glaze materials or protective coatings on ceramic and glass products. This creates shiny surfaces that are scratch-resistant.
Mold Preheating: In glass production processes, burners are used to heat molds before the introduction of molten materials to reduce sudden thermal changes.
Features of Furnace Burners in Glass and Ceramics Industries
In glass and ceramics sectors, furnace burners are crucial for enhancing thermal processes, such as:
- Consistent heat production for superior product quality
- Accurate flame control to avoid cracking and harm


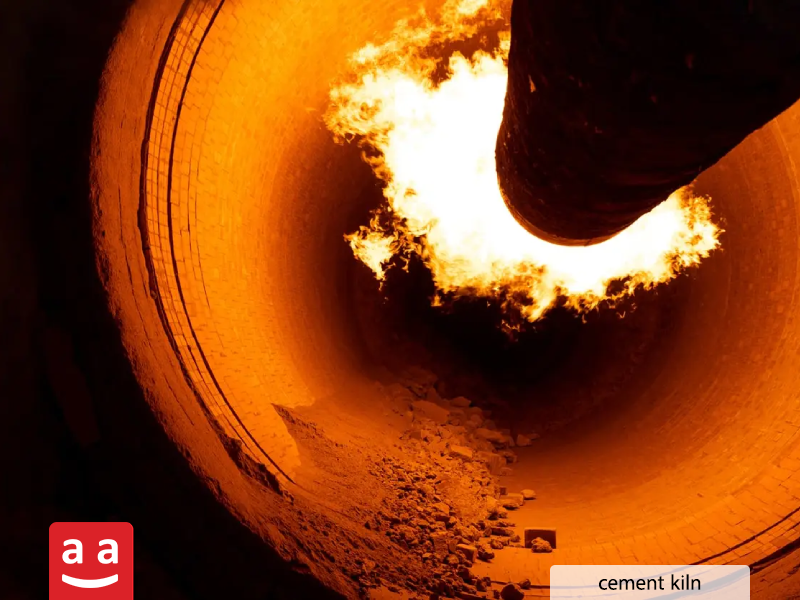
Plaster and Cement
In cement and plaster industries, furnace burners provide the necessary conditions for various processes by generating high and uniform temperatures. Their main applications include:
Clinker Firing in Cement Industry: Burners provide the necessary heat in cement rotary kilns to convert raw materials (limestone and clay) into clinker. This temperature typically exceeds 1400 degrees Celsius.
Limestone Calcination: In preheaters and calciners, burners facilitate the removal of carbon dioxide from limestone, preparing it for introduction into cement kilns.
Plaster Production: In the gypsum calcination process, burners provide the necessary heat to remove water from gypsum rock (calcium sulfate) and convert it into building plaster.
Raw Material Preheating: Burners are used to heat the incoming raw materials for the kilns, reducing energy consumption and increasing efficiency.
Features of Furnace Burners in Cement and Plaster Industries
Furnace burners play a key role in the production of cement and gypsum and optimize the production process with the following features:
- High temperature: Ideal for demanding thermal processes
- Uniform flame: Ensures the quality of the final product
- High durability and efficiency: Suitable for harsh industrial conditions


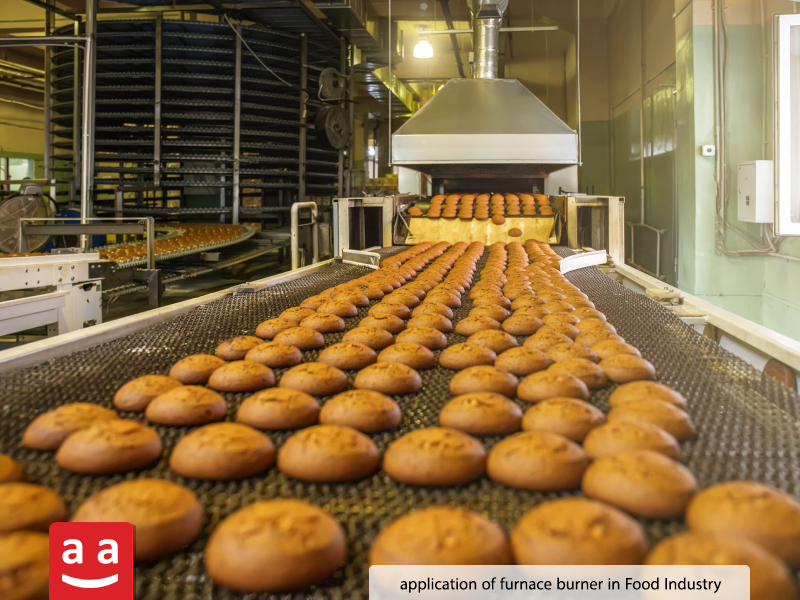
Food and Beverage
In food and beverage sectors, furnace burners are utilized to supply heat for production, cooking, and packaging processes. These burners significantly contribute to quality and efficiency optimization due to their ability to precisely control heat and flame. Key applications include:
Baking: Burners are used in industrial ovens and furnaces for baking various breads, cakes, cookies, and other food products. Precise temperature control is essential to ensure uniform baking.
Pasteurization and Sterilization: Burners supply the heat required in processes like milk and juice pasteurization and sterilizing packaged food products, ensuring the removal of microbes and enhancing longevity.
Food Drying: In industrial drying machines, burners facilitate the reduction of moisture content in products like dried fruits, vegetables, coffee, and tea.
Steam Production: Burners are used in steam boilers to generate steam for processes in food production, beverages, and cleaning industrial equipment.
Direct Heating in Beverages: Industrial burners are used to heat tanks and processes such as coffee brewing or beer production.
Features of Furnace Burners in Food Industry
Industrial burners play a crucial role in food sectors by ensuring product quality and compliance with hygiene standards, thanks to their distinct features. The main characteristics of these burners include:
- Precise temperature control: To maintain quality and prevent burning
- High hygiene and safety: In accordance with food industry standards
- Uniform flame: Ensures the quality of thermal processes


Paper and Printing
Industrial burners find applications in the paper and printing industries, with key uses including:
Paper Drying: Burners provide the necessary heat for drying paper in production and processing machines. This process helps remove moisture and increase the strength of the paper.
Cylinder Heating: In paper production machinery, heating cylinders utilize the heat generated by burners for the processes of smoothing and stabilizing the thickness of the paper.
Ink Stabilization: Burners are used in the printing process to quickly dry and stabilize ink on the paper. This improves the quality and longevity of the print.
Key Attributes of Industrial Burners for Paper and Printing Applications
Industrial burners in paper and printing industries ensure the quality of the final product by providing precise and uniform heat. The main features of these burners include:
- Uniform heat: Ensures the quality of the final product
- Precise temperature control: To prevent damage to paper and printing
- Longevity and reliability: Appropriate for continuous operations
Types of Industrial Furnace Burners
Industrial furnace burners are designed to meet a wide variety of operational requirements, and they can be installed either vertically or horizontally depending on the specific furnace design. They are further classified into the following types, each tailored to distinct industrial needs:
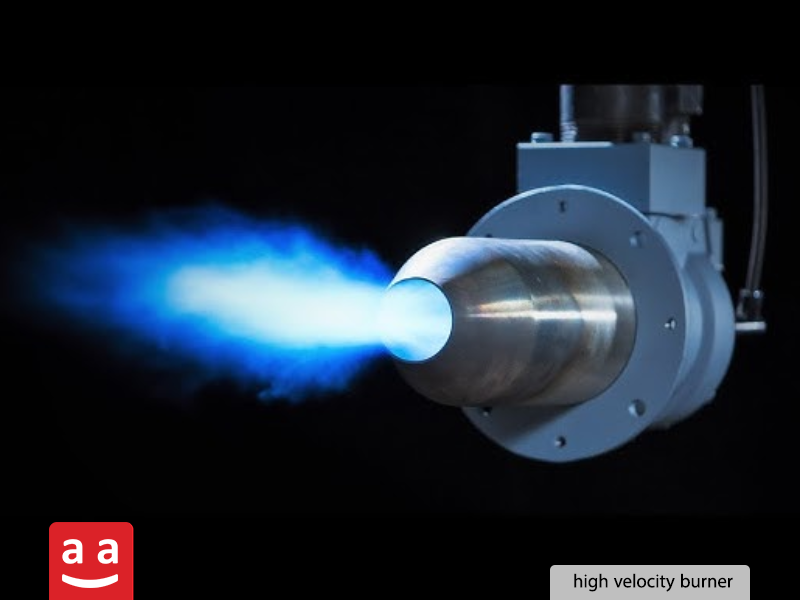
High Velocity Burners
These burners are specifically designed for applications that need a high output velocity of combustion gases (usually between 70 to 250 meters per second). They are well-suited for improving heat transfer and achieving even temperature distribution in kilns like those used for ceramics and glass.


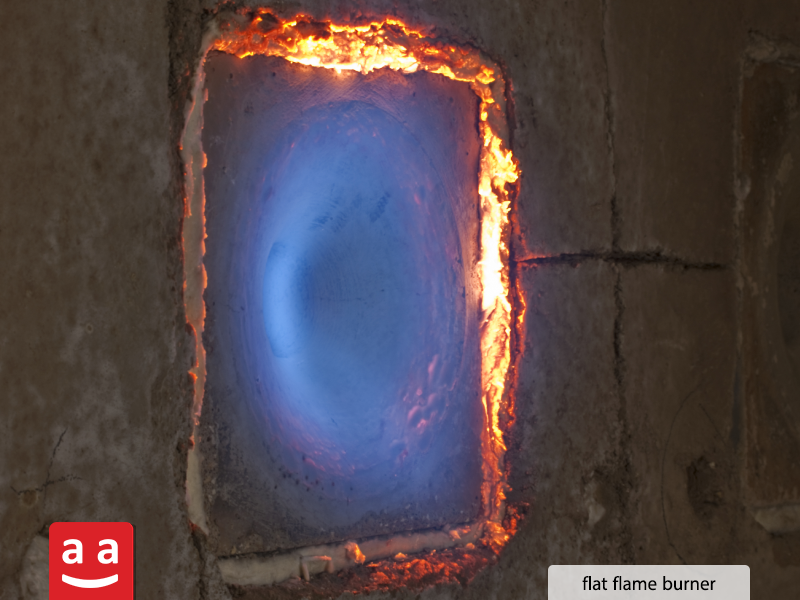
Flat Flame Burners
Flat flame burners generate a flat and even flame, ideal for processes that need controlled temperatures and uniform heat distribution, where components must not directly contact the flame. The combustion air is released from the burner nozzle in a swirling motion at high speed to create a flame that opens up and forms close to the wall. Additionally, the output of the burner’s refractory block is shaped like a parabolic indentation, which aids in flame shaping. These burners are primarily used in the aluminum, glass, and ceramics industries.


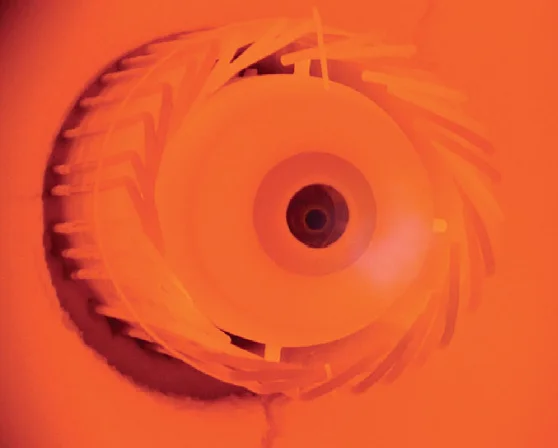
Flameless Burners
Flameless combustion, also known as MILD combustion or HiTAC (High Temperature Air Combustion), is a technique where the flame is invisible to the naked eye. The primary advantage of this method is that it leads to extremely low levels of NOx and CO emissions due to the homogeneity of the flame temperature and efficient mixing of reactants. Achieving flameless combustion is possible through various methods such as oxygen dilution (MILD), air preheating (HiTAC), and colorless distributed combustion (CDC). Flameless combustion is preferred in many industries due to its environmental benefits, particularly in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.


Oxygen-Enriched Burners
Oxygen-enriched burners enhance the combustion process by injecting pure oxygen into the burner, increasing flame temperature and thermal efficiency. These burners can operate using an air-oxygen mixture (air-oxy fuel burners) or exclusively with oxygen (oxyfuel burners). Oxyfuel combustion is especially beneficial in reducing NOx emissions because nitrogen, a primary component in NOx formation, is absent from the reactants. This method is highly effective in industries where high temperatures are required, such as steel production and glassmaking.


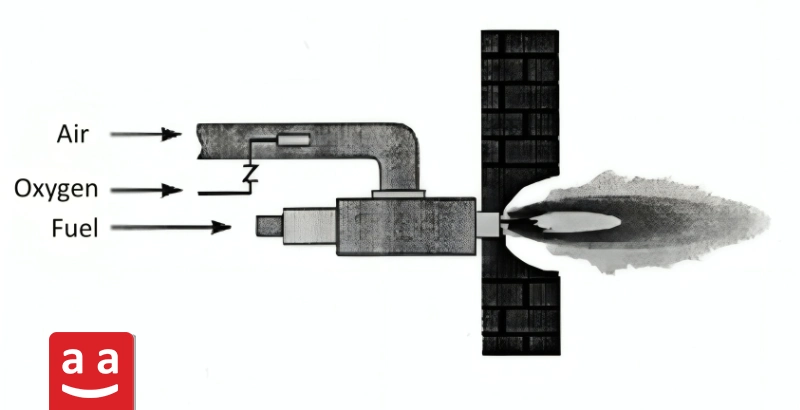

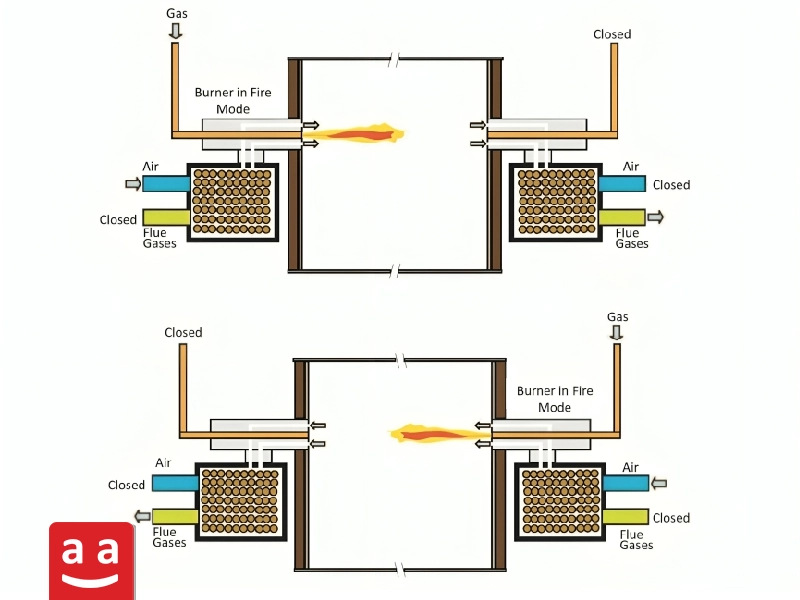
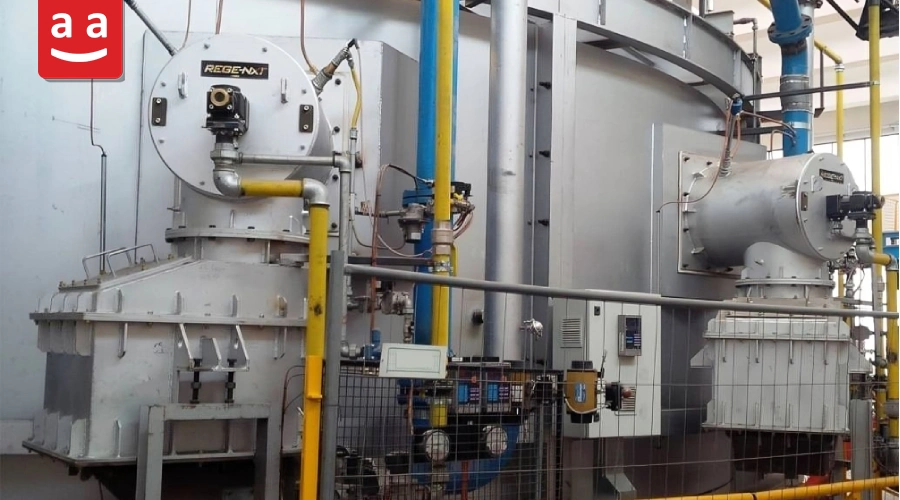
Regenerative Burners
These burners are installed in pairs, with each burner having a heat storage tank. They operate alternately, meaning that at any given moment, one burner is active while the other is inactive. The combustion products from the active burner flow through the other burner and its heat storage tank, allowing a portion of the heat in the combustion products to be captured. Then, the first burner is turned off, and the second burner is activated.
In regenerative burners, the combustion air flows through a heat storage tank before entering the combustion head, where it gets preheated by absorbing heat. This process is continuously repeated, resulting in the recovery of some heat from the combustion products, ensuring that the inlet air to the burners is consistently preheated. These burners are utilized in industries like glass and metals.

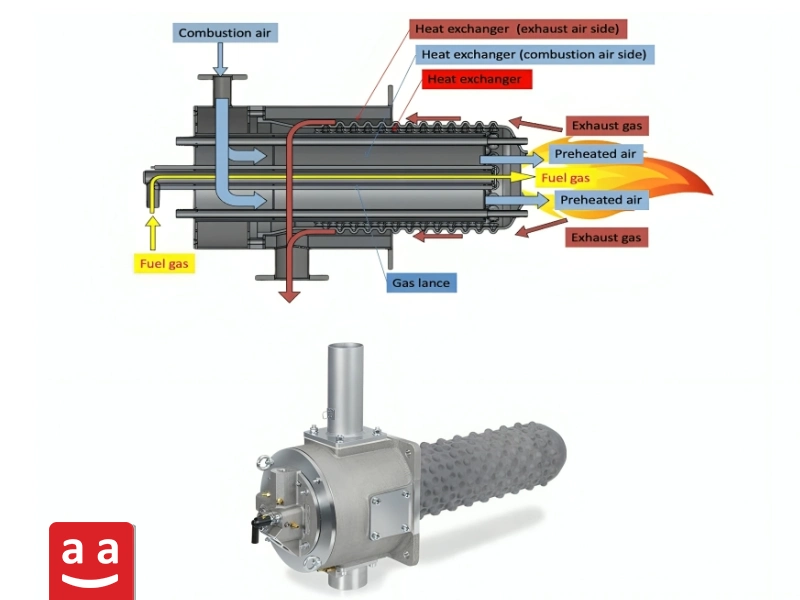
Self-Recuperative Burners
Recuperative burners are similar to regenerative burners in that they recover heat from the exhaust gases, but they incorporate the heat exchanger directly into the burner design. This allows for preheating of combustion air, fuel, or both, using hot combustion products. While recuperative burners may not achieve the same level of efficiency as regenerative systems, they offer a compact solution that eliminates the need for external heat exchangers, making them ideal for smaller or lower-temperature processes.



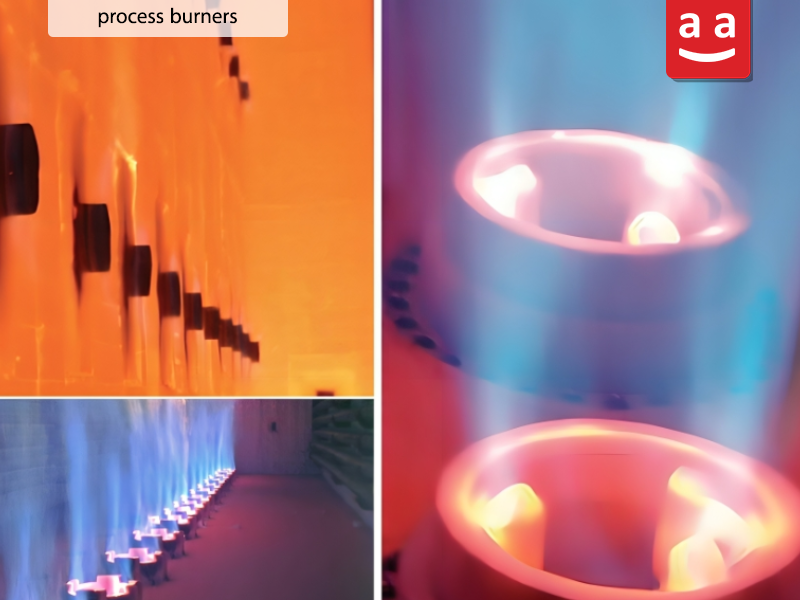
Process Burners
Process burners are applicable for heating process fluids within petroleum, gas, and petrochemical industries. They can operate without fans, using natural flow, or with fans, and are available in various types, chosen based on the specific process and furnace conditions.
Raadman process burners are among the best options for use in furnaces and heaters in gas, oil, and petrochemical industries, specifically designed to meet the conditions of these sectors. The RSun series burners by Raadman are used in fired heaters and similar furnaces, generating very low emissions thanks to their distinctive flame shape. Furthermore, the RShine series burners, classified as radiant wall types, are employed in reformers or other furnaces requiring consistent heat. The application of these burners in the gas, oil, and petrochemical industries enhances processes, increases efficiency, and reduces fuel consumption.


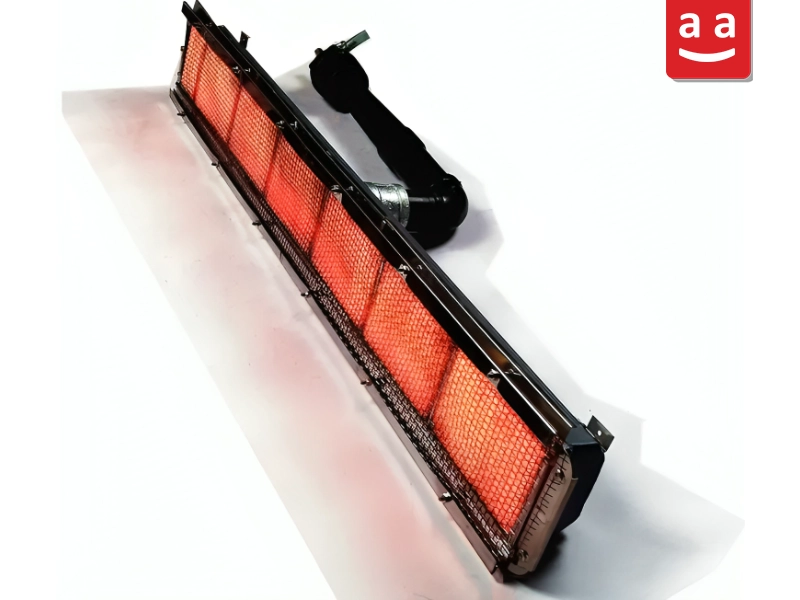
Infrared Burners
Infrared burners belong to the premixed category and are equipped with a porous metal or ceramic material where combustion occurs. The heat produced leads to the melting and glowing of the porous solid, which then radiates the absorbed heat. These burners are utilized in the food sector and in the paper and printing industries.


Advancements in Industrial Burner Technology
As the demand for energy continues to rise, industrial furnaces and their burners must meet the challenges of efficiency and sustainability. The integration of technologies like self-recuperative burners, which combine burner components and heat exchangers in a single package, has enhanced the performance of radiant tube systems. These advancements reduce energy loss and improve heat recovery.
Furthermore, the use of advanced materials in burner construction, such as ceramics for high-temperature applications, has allowed burners to operate more efficiently at higher temperatures, improving overall system performance. As industries seek to minimize their environmental impact, innovations in burner design and operation will play a key role in achieving cleaner, more efficient combustion processes.
Industrial Furnace Burner: An Important Device for Improving Efficiency and Quality in Industries
Industrial furnace burners are essential components of modern industry, powering processes ranging from petrochemicals and steel production to glass manufacturing and food processing. Therefore, choosing the most suitable type of furnace burner based on the needs of each industry is an effective step toward enhancing production quality and quantity, reducing costs, and protecting the environment. As industries try to meet increasingly stringent environmental standards, using advanced burner systems will help to reach this goal.
Raadman, with its modern design of industrial furnace burners and the implementation of up-to-date technologies, is recognized as one of the most reputable manufacturers of industrial burners today. Raadman burners utilize the latest combustion technologies to reduce pollutants, enhance thermal efficiency, and improve overall performance across various industries. Choosing a suitable furnace burner from reputable brands like Raadman can significantly contribute to increased productivity and reduced operational costs.






2 responses
I am looking for 2 ovens combustion air fuel industial furnace burners. Paraffin and air mixture, 2 ovens, 3x3x 1,2m (2off burners)and 4,2×3,2×1,2m(4 burners)
Thank you for your comment.
For more information and product inquiries, please feel free to contact our sales department using the details below
http://[email protected]
+98 913 429 4965
Telegram: @raadmansales