Hospitals are critical institutions, and their boiler rooms play an equally significant role. In other words, hospital boiler room serves as its heart and central organ. Now that the significance of these facilities has been discussed, a question may arise: What is the function of a hospital boiler room? A boiler room is responsible for managing the operation of heating, cooling, air conditioning, and hot water supply systems. This directly impacts the comfort of patients and staff as well as the quality of healthcare services. For this reason, precise design and adherence to quality standards in hospital boiler rooms are necessary.
An Introduction to components of a hospital boiler room
Hospital boiler room, as the heart of heating, cooling, and ventilation systems, is responsible for providing energy and creating a comfortable environment within hospital settings. The components of a hospital boiler room generally include: hot water and steam boilers, pumps, piping systems, heat exchangers, fuel tanks, expansion tanks, chillers, controllers, and automation equipment.
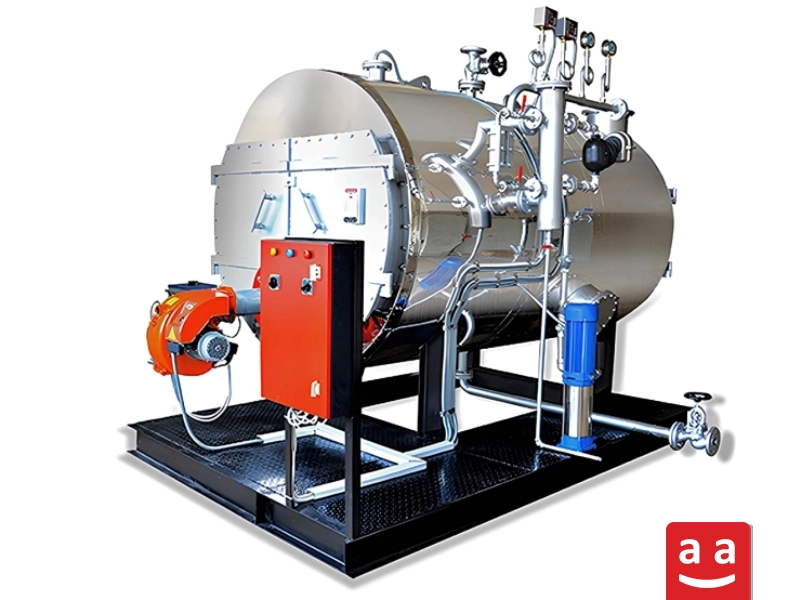

Steam and hot water boilers
Hot water and steam are crucial for all healthcare activities and hospital treatment processes. To generate steam and hot water, there must be a mechanism that can provide the necessary heat. For this purpose, steam and hot water boilers, which are among the most important components of a hospital boiler room, are used to supply hot water or steam. Water heating inside the boilers and its transformation into hot water or steam is done by a burner. An industrial burner mixes various fuels, such as natural gas, oil, etc., with air in the correct ratio. The combustion process then occurs, producing a flame.
During combustion, the thermal energy of fuel is released, producing heat. In boilers, this heat is used to generate steam or hot water. The importance of the boiler and industrial burner is such that having a backup package (a set of boiler and burner) in hospital boiler rooms is crucial. The following outlines the most important functions of a boiler.
- Providing heat for buildings: A key application of hot water boilers in a hospital is to heat the interior spaces of the building. The hot water produced by the hot water boiler is transferred through the piping system to air handling units or fan coils throughout the building.
- Providing hot water for HVAC systems: Maintaining an appropriate temperature inside hospitals is crucial. To regulate the desired temperature for the hospital’s indoor environment, air conditioning systems like air handling units are used. The hot water generated by the boiler is transferred through the piping system to the coil in the air handling unit. As air flows over the coil, it is heated to the desired temperature for the comfort of individuals in the hospital.
- Sterilization: Medical equipment and tools, especially those used in surgeries, must be sterilized before use. The steam produced by the boiler is pumped into a disinfection device known as an autoclave. This device is typically found in laboratories or surgical units. The hot steam sanitizes surfaces, eliminating harmful microorganisms. Additionally, it is a safer alternative compared to chemical methods.
- Providing Sanitary and Medical Hot Water: The constant need for hot water in hospitals is an important factor to consider. Thus, a hot water boiler is an appropriate solution for providing the necessary hot water for sanitation and medical purposes in hospitals.
- Laundry Process: In laundry rooms, a significant amount of patient gowns, bed sheets, and towels are washed daily. The hot water and steam boiler must provide the necessary hot water or steam for washing clothes, linens, etc. It is common for the hospital laundry room to have its own boiler, emphasizing the importance of using hot water and steam boilers in this section.
- Kitchen: Cooking is another important consideration in hospitals. Kitchen staff is responsible for preparing food for patients, visitors, and other hospital personnel. Naturally, the preparation of such a large amount of food requires a considerable amount of hot water.
Piping system
This system includes pipes for water, steam, gas, and sewage. The piping system in the hospital boiler room is designed to supply drinking water, hot water for heating systems, and to drain sewage.

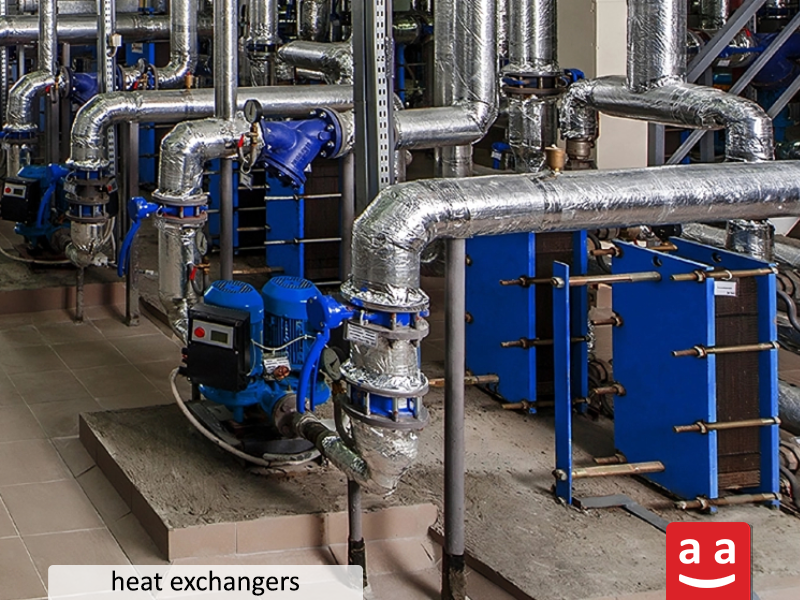
Heat exchangers
One of the key components in a hospital boiler room is a heat exchanger. The function of a heat exchanger is to transfer heat between two mediums (such as water and air). Heat exchangers play a crucial role in the boiler room by facilitating heat exchange between different fluids. These devices are used to optimize energy use and increase the efficiency of heating and cooling systems. It is worth mentioning that proper management and regular maintenance of these heat exchangers are crucial for ensuring their optimal performance.

Pumps
These devices are responsible for transferring and circulating fluids (such as hot and cold water) in the heating, cooling, and domestic hot water systems. Pumps generate the necessary pressure to move the hot water produced by the boilers to air handlers, fan coils, or other parts of the hospital. In cooling systems, pumps also transfer the cold water produced by chillers to the HVAC systems. Thus, pumps play an essential role in optimizing the boiler room’s performance and efficiently distributing heat and cold to various areas of the hospital, ensuring proper environmental conditions for both patients and staff.
Fuel sources
Industrial burners in boilers use various fuel sources to generate heat. It is worth mentioning that a dual-fuel industrial burner could be a better option for a hospital boiler room. In this case, the limitation of one fuel source will not disrupt the operation of the boiler room, as another fuel can be used as a replacement. Raadman dual-fuel burners, available in all capacity ranges, is an intelligent choice for boilers in a hospital boiler room. Fuel source selection in a boiler room is generally determined by the type of energy systems and the specific requirements of the hospital. Some common fuel sources are listed below:
1- Natural gas: This type of fuel is widely used as an economical and common fuel for burners in hot water and steam boilers. Natural gas prevents excessive air pollution and contributes to reducing operational costs.
2- Oil: It is another common fuel used for hot water and steam boilers. Compared to natural gas, oil produces more pollution. It is generally used in areas where access to natural gas is limited and requires storage and maintenance.
3- Electricity: Electric boilers are used in certain hospital boiler rooms as well. Since they operate on electricity rather than fossil fuels, they substantially decrease the release of pollutants and greenhouse gases. Nevertheless, these boilers are typically used for restricted applications due to the high expense of electricity.

Expansion tanks
One of the key components in the systems of a hospital boiler room is an expansion tank. Expansion tanks play a vital role in managing water pressure in both heating and cooling systems. This tank is specifically designed to compensate for the expansion of water due to temperature changes. In fact, as the temperature increases, the volume of water expands significantly. If there is insufficient space for this volume increase, the internal pressure of the system rises dramatically. This can result in damage to the boiler, pipes, and other related equipment.
An expansion tank provides an adequate space to absorb the excess water resulting from thermal expansion, allowing water to expand freely. This mechanism effectively prevents excessive pressure buildup in the system, ensuring the safety and efficiency of the heating or cooling system.
The expansion tank also serves to provide additional water when needed; in cases where the system requires an increase in water volume, the tank can return extra water to the system. This ensures proper water circulation and contributes to maintaining the hydraulic balance of the system. Typically, these tanks are installed close to boilers and pumps to reduce pipe length and optimize system efficiency.

Chiller
A chiller is a device used to produce and supply chilled water for cooling the interior of buildings, factories, and hospitals. It is commonly used in central air conditioning systems and plays a critical role in maintaining the required temperature and humidity in large spaces. The chiller operates on the thermodynamic refrigeration cycle. Initially, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the water in the evaporator, causing it to evaporate and transform into a gas. This gas is compressed in the compressor, increasing its temperature and pressure. It then flows to the condenser, where it releases heat to the surroundings and condenses back into a liquid. The liquid refrigerant is passed through an expansion valve, where its pressure and temperature drop. The cold refrigerant then returns to the evaporator, and the cycle repeats. The application of chillers in hospitals are as follows:
1- Hospital environment cooling: Cooling the hospital environment using a chiller and air handling unit (AHU) is one of the most important and effective methods for creating optimal temperature and humidity conditions in healthcare spaces. The chiller serves as the source for producing cold water, which is transferred to the air handling units. The AHUs use this cold water to cool the indoor air of the hospital and distribute it to various areas, including patient rooms, operating rooms, and intensive care units.
2- Advanced medical equipment cooling: X-ray machines, linear accelerators, and lasers generate a significant amount of heat during their operation. To maintain their efficiency and proper functioning, continuous and effective cooling is required, which is the responsibility of chillers. By supplying chilled water, chillers help these devices operate at optimal temperatures and prevent damage caused by excessive heat.

Controllers and automation equipment
In hospital boiler rooms, controllers are vital for enhancing the efficiency of heating, cooling, and air conditioning systems. These controllers function as part of the Building Management System (BMS), enabling the integration and intelligent control of all equipment. They may include Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC), which are responsible for managing complex processes and controlling various equipment such as boilers and chillers.
These controllers facilitate energy efficiency, cost reduction, and maintaining optimal environmental conditions for patients and hospital staff. Furthermore, the monitoring and alarm capabilities of the controllers help managers and technicians in responding quickly to issues, preventing equipment damage. Overall, controllers contribute to optimizing the operation of the boiler room and enhancing comfort within the hospital environment.

The Role of Smart Systems in Improving the Performance of Hospital Boiler Rooms
A Building Management System (BMS) is a centralized smart system designed to monitor, control, and optimize the performance of electrical and mechanical equipment in a building. It automatically manages various components such as HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), lighting, emergency power, fire detection and suppression systems, and more, to ensure safe, efficient, and optimized operations.
In a hospital’s boiler room, a smart control system plays a critical role in regulating the performance of heating and cooling systems, pumps, and other mechanical equipment. By using sensors installed throughout both the interior and exterior of the building, the system automatically detects the environmental thermal needs and activates or deactivates relevant equipment accordingly.
This not only leads to a noticeable reduction in energy and fuel consumption but also significantly minimizes equipment wear and tear by preventing unnecessary operation. For example, during nighttime or off-hours—such as in hospital administrative areas—the boiler room might continue running without interruption, wasting energy and generating unused heat. This not only results in energy loss but can also negatively impact indoor thermal comfort.
Therefore, implementing smart management systems equipped with environmental temperature sensors is strongly recommended as an effective solution. These systems dynamically adjust equipment performance based on real-time conditions, ultimately maximizing energy efficiency.
Raadman Industrial Burners, equipped with AutoFlame smart systems, are capable of integrating with a BMS (Building Management System). By receiving commands directly from the BMS, they can precisely control the fuel and air input to the burner. This integration not only reduces fuel consumption but also extends the lifespan of the boiler equipment.
Hospital Boiler Room; guaranteeing Sustainable and safe performance
As the heart of mechanical and energy systems, a hospital boiler room is essential for maintaining optimal conditions for patients and staff. It ensures the provision of heating, cooling, ventilation, and hot water, thereby supporting the quality of healthcare services. Advancements in technology and the growing demands of hospitals have made it possible to optimize operations and reduce energy usage through Building Management Systems (BMS) and smart controllers.
Moreover, proper selection of fuel sources and efficient equipment in hospital boiler rooms can minimize environmental impact and operational expenses. In conclusion, efficient management and maintenance of boiler rooms not only enhance the comfort and health of patients and staff but also elevate the overall performance and service quality of hospitals.