Refinery and petrochemical units, as critical pillars of the energy and chemical industries, depend heavily on thermal systems, particularly burners. Fired heaters are used to increase the temperature of process fluids, while reformers use burners to provide the energy necessary for chemical reactions. This burner must provide sufficient heat while also being optimized for fuel consumption and emissions. This article examines and analyzes various types of petro-refinery burners used in petrochemical plants and refineries, with a special focus on the products of Raadman Company.
Different Types of Furnaces
In this part, different types of furnaces used in petrochemical and refinery units are reviewed. Due to the variety of these furnaces, corresponding petro-refinery burners are also used, which will be introduced in the subsequent sections.
Fired Heater
In chemical and petrochemical plants, fired heaters are considered one of the key equipment for providing the heat required in various processes. They are designed to heat process fluids—such as hydrocarbon streams to specific temperatures. In fired heaters, heat is transferred directly through fuel combustion; hence, the term fired heater, meaning “direct-flame heater,” is used. The type of petro-refinery burners used in a fired heater plays a crucial role in flame control, efficiency, and reducing emissions.
In the article ” What is a Fired Heater? “, you will find comprehensive and detailed information about fired heaters, how they work, and their various industrial applications. We highly recommend reading this article.
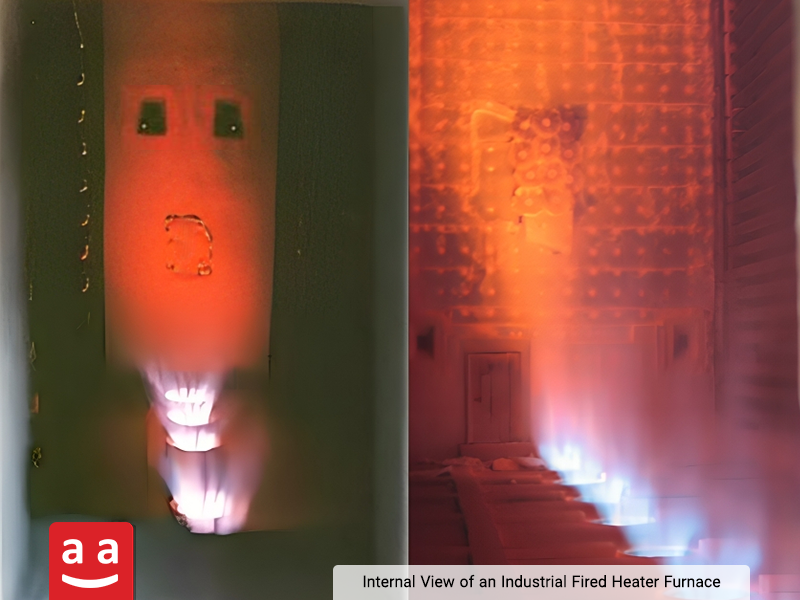


Reformer Furnace
Reformers play a crucial role in petrochemical units by providing the heat required for endothermic reactions. These units are typically used to convert natural gas or other hydrocarbons into synthesis gas (syngas), which consists of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide. The syngas produced by reformers is the fundamental feedstock for producing methanol, ammonia, and various other chemical products.
Reforming process generally occurs at high temperatures (up to 1000°C) and requires efficient and uniform heat transfer to the feed-containing tubes. This heat is supplied by burners installed on the walls, roof, or floor of the reformer furnace. The type and performance of these burners have a direct impact on process efficiency and emissions control.
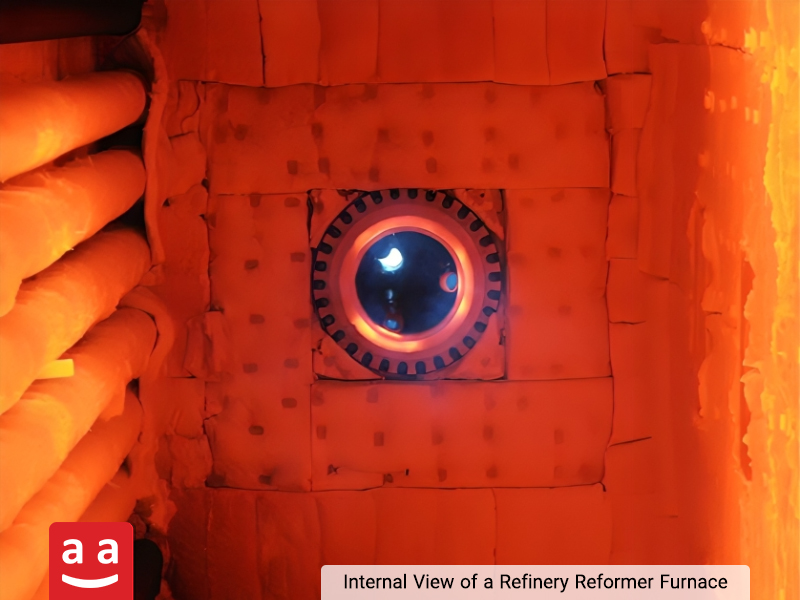

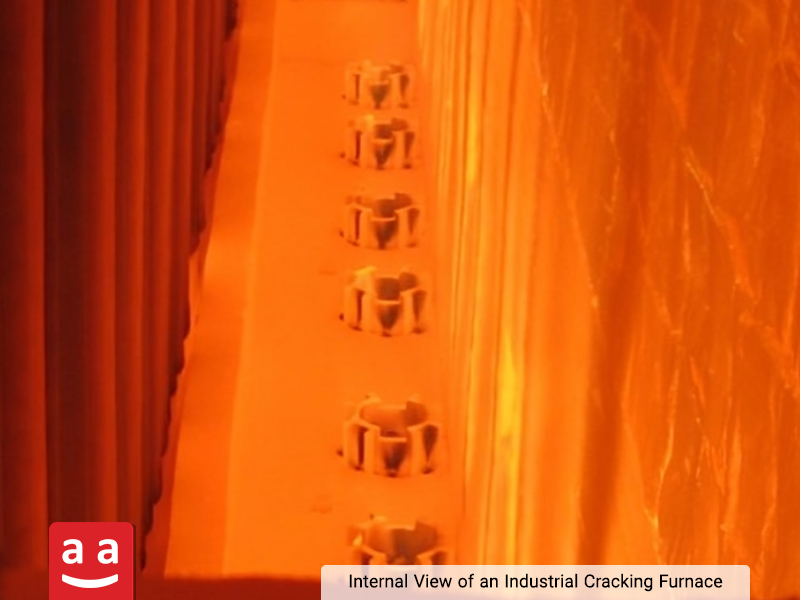
Cracking Furnace
Cracking furnaces are key equipment in olefin production units and play a fundamental role in the petrochemical industry. These furnaces are responsible for breaking down heavy hydrocarbon molecules, such as naphtha, ethane, oil, and others, under high-temperature conditions, converting them into lighter compounds like ethylene, propylene, and other raw materials used in the production of plastics and chemical products
Steam cracking process, the most common cracking method, operates within a temperature range of 750 to 850°C. Given the high sensitivity of the reactions and the possibility of coke or soot deposition, precise thermal management and uniform temperature distribution are crucial. Therefore, choosing a suitable petro-refinery burner that can generate a stable, uniform, and low-pollution flame is essential for achieving optimal furnace performance.


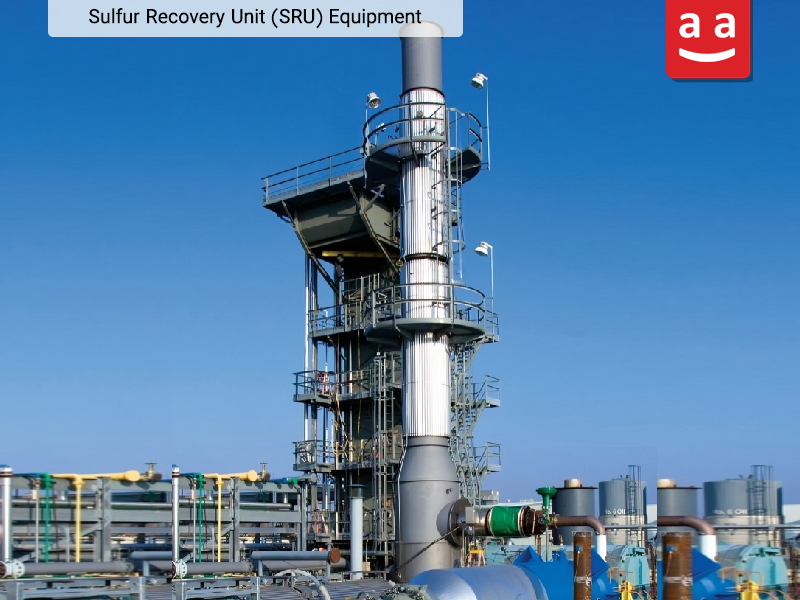
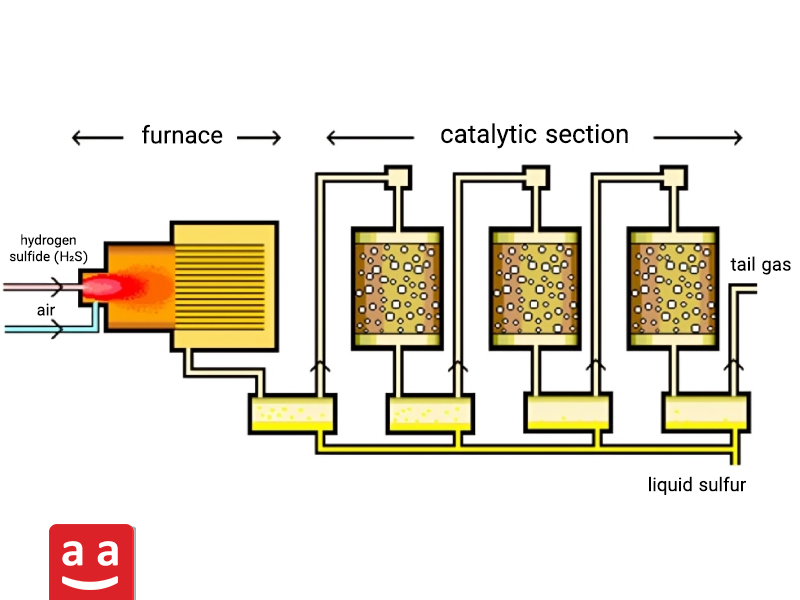
Sulfur Recovery Unit (SRU) Furnace
Sulfur recovery furnaces used in Sulfur Recovery Units (SRU) are designed to convert acidic gases into elemental sulfur. During the process, gases containing hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), found in natural gas and petroleum refining byproducts, enter a thermal reactor where a portion is oxidized to sulfur dioxide (SO₂) through combustion. These two compounds subsequently react in later stages to produce elemental sulfur. The advanced combustion system design in these furnaces ensures that the conversion reactions of hydrogen sulfide to elemental sulfur occur under optimal thermal and dynamic conditions.
SRU furnaces, with their robust construction, not only achieve high efficiency in sulfur recovery but also prevent corrosion caused by the acid dew point thanks to their special design. These features make them vital components in refineries for controlling sulfur pollutants and producing commercial sulfur.



Different Types of Burners
After reviewing the various types of furnaces used in petrochemical and refinery units, it is now time to analyze the petro-refinery burners used in these furnaces. Despite differences in furnace design and application, the burners used in these units share a relatively common structure. Typically, the inlet gas pressure drop in these burners is deliberately engineered to be high, increasing the flow velocity at the nozzle. This increased gas velocity in the nozzle area enhances the mixing of fuel and air, thereby creating the optimal conditions for forming a stable and uniform flame.
Burners for Fired Heater
Burners used in fired heaters are designed to provide the required process heat with appropriate efficiency and minimal emissions. These burners are generally installed on the fired heater’s floor or walls and provide thermal energy for heating process fluids by fuel combustion. Fired heater burners are divided into natural draft and forced draft categories according to their combustion air supply. Forced draft burners use a fan to induce airflow, while natural draft burners rely on natural suction to draw combustion air into the fired heater. This suction is caused by the density difference between the hot furnace gases and the ambient air, creating airflow into the unit.
R-Sun burner, manufactured by raadman, is a process burner intended for fired heater applications in petro-refinery sectors. This burner is well-known for its specially designed tile; the tile creates a corrugated flame and increases the contact surface area, enhancing gas mixing and consequently reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions. Alongside staging fuel injection, this special tile design makes the Arsan burner an ultra-low NOx burner.
This petro refinery burner can handle different gaseous fuels including natural gas, hydrogen mixtures with hydrogen content up to 70%, refinery gas, and petrochemical off-gases. The combustion air for the burner can be provided through forced draft or natural draft, and can also be supplied as preheated air.
In addition to R-Sun burner, R-Flex burner is presented as one of raaadman’s dual-fuel burners for fired heater applications. This burner can operate using either natural gas or oil.
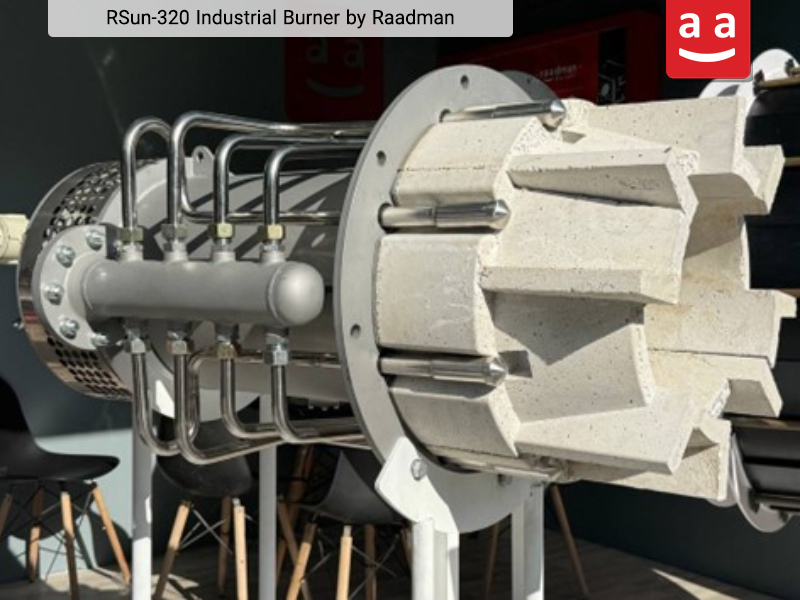


Radiant Wall Burner
These burners are used in combustion systems that require a flat and radiant flame. These burners are installed on the internal walls of furnaces and transfer heat by heating the wall surface, which then radiates thermal energy to the tubes containing feedstock inside the furnace. Their operation is especially efficient in furnaces with small combustion zones, making them well-suited for reformer and cracking furnace applications.
One of the radiant wall burners designed by Raadman Industrial Group is the R-Shine burner, which holds a distinguished position among radiant burners due to its engineered design and optimized performance. The R-Shine burner is produced with capacities of up to 1 MW and supports a variety of gaseous fuels, including natural gas, purge gas, hydrogen-containing mixtures, and refinery waste gases. Its unique design creates a symmetrical flame, ensuring uniform heating of the furnace wall.
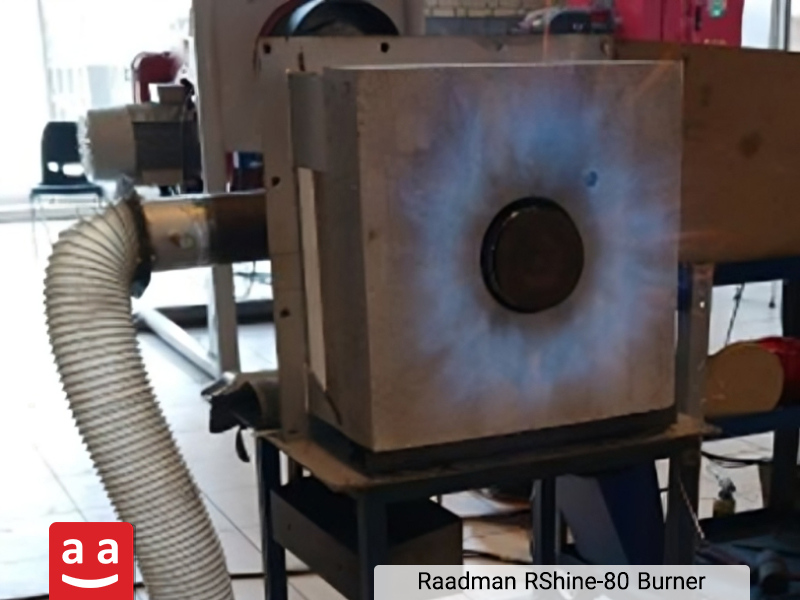


Arc Burner
Arc burners are specifically designed for applications that require a flame directed from top to bottom. These burners are mounted directly on the furnace ceiling and direct the flame downward. They are ideal in areas where wall or floor mounting is not feasible due to spatial limitations. Therefore, Arc burners are a suitable choice for petrochemical furnace ceilings, especially in reformer and cracking furnaces, and are classified as petro-refinery burners.
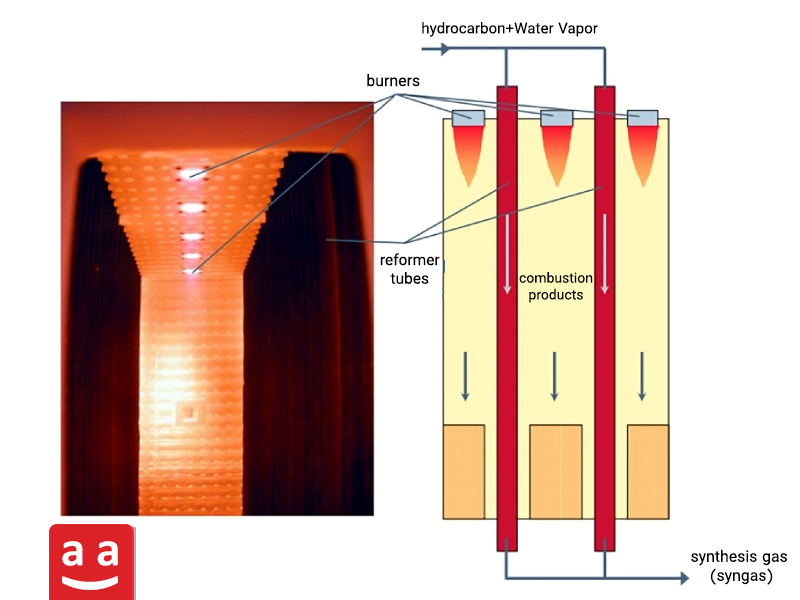

R-Arc burner, part of raadman industrial group’s arc burner series, uses forced draft (FD) fans to supply combustion air, enabling precise control of the air-to-fuel ratio and flame stability. This petro-refinery burner can operate with a wide range of gaseous fuels including natural gas, purge gas, hydrogen-containing blends, and petrochemical off-gases. R-Arc burners are produced with capacities up to 4 megawatts and are optimized to deliver a stable and uniform flame with minimal emissions, particularly in terms of nitrogen oxides (NOx) output.
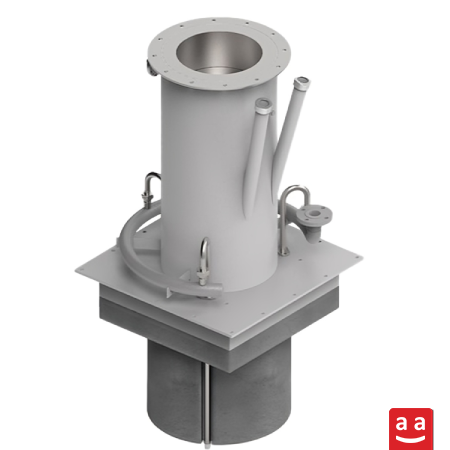


Burner for Water-tube Boiler
One of the key applications of petro-refinery burners in petrochemical and refinery plants is in water-tube boilers. In these systems, the heat generated by the burner is transferred to the external surface of tubes through which water flows. Depending on the boiler design, the water is either heated or converted into steam.
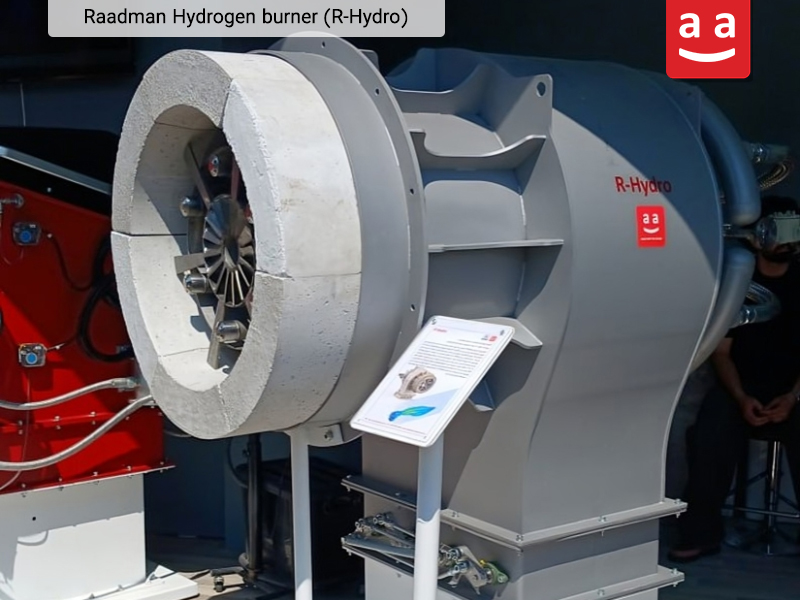
R-Hydro burner, developed by raadman industrial group, is specifically engineered for use in water-tube boilers. It can burn a broad spectrum of gaseous fuels, including 100% hydrogen, natural gas, purge gas, and petrochemical waste gases. Designed to match the combustion chamber geometry of water-tube boilers—usually large in diameter and short in length—the R-Hydro burner provides efficient operation and meets domestic industry demands. R-Hydro burners are available up to 40 MW capacity and produce very low NOx emissions thanks to hydrogen fuel.

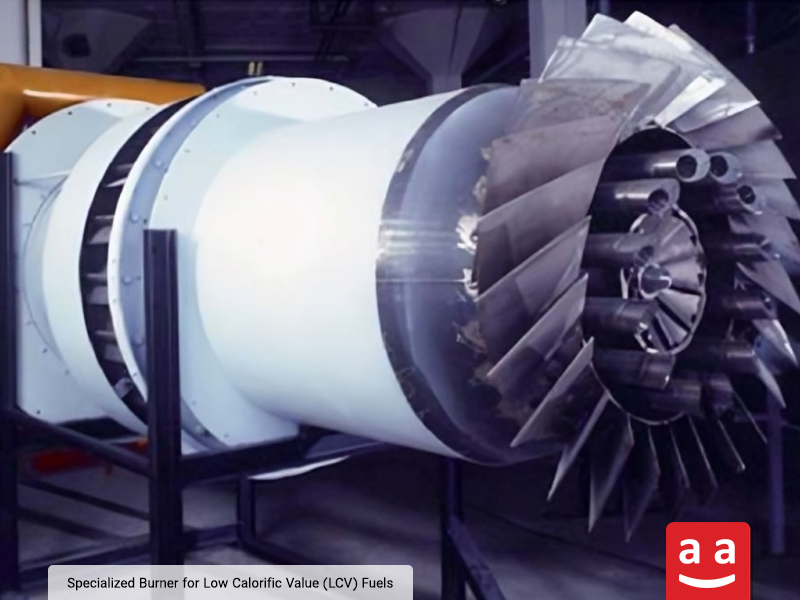
Low Calorific Value (LCV) Burner
In some industrial processes, synthesis gas or recycled gas streams are generated with features such as high temperature, low pressure, and, importantly, very low heating value. These gases lack the ability to sustain stable flames under standard conditions, and improper use results in complete energy loss. To combust these low-calorific-value gases effectively, specialized petro-refinery burners termed Low Calorific Value Burners are utilized.
This petrochemical burner is specifically designed to maintain a stable and secure flame in demanding combustion environments, effectively recovering energy from low-calorific-value gases. It is commonly used for combusting off-gases from sulfur recovery units, processed flare gases, and low-grade byproduct gases in refinery and petrochemical processes.


Final Remarks: The Significance of Petro-Refinery Burners in Industrial Process Optimization
In the petrochemical and refining industries, petro-refinery burners are critical parts of thermal systems, playing a vital role in delivering safe, stable, and efficient heat for process operations. A close analysis of burners used in various furnaces, such as fired heaters, reformer furnaces, cracking units, water-tube boilers, and sulfur recovery units, reveals that choosing the right burner significantly influences not only thermal efficiency, but also emissions control, fuel economy, and equipment durability. Moreover, the ability of these burners to handle a wide range of fuels, including natural gas, refinery off-gases, purge gas, hydrogen blends, and low-calorific-value gases, highlights the importance of flexible engineering and advanced burner design in modern process facilities.
Raadman Industrial Group has effectively addressed the diverse needs of the country’s process industries by developing burners such as R-Sun, R-Shine, R-Arc, and R-Hydro. These products embody a forward-thinking approach to combustion technology, with a strong focus on emission reduction, flame shape optimization, compatibility with alternative fuels, and the adoption of innovative design solutions.