premixed = premix = pre-mixed
In today’s progressive world where we live, air pollution is the most severe problem in human societies. Domestic powerhouses and burners have a significant contribution to air pollution. Dilution processes such as FGR or water and vapor injection are the latest technologies that significantly reduce NOx.
Nowadays, new premixed combustion technologies can reduce NOx and CO emissions simultaneously. You may be asked this question, what is premix combustion technology, and how does it mitigate hazardous combustion emissions?
Based on fuel and air mixing location, burners are divided into two classes: nozzle mixed and premixed burners. These burners are defined according to the BS EN 676 (2020):
Nozzle Mixed Burners: burner in which part, or all, of the air required for combustion of the gas, is mixed with the gas at, or downstream of, the air and gas ports.
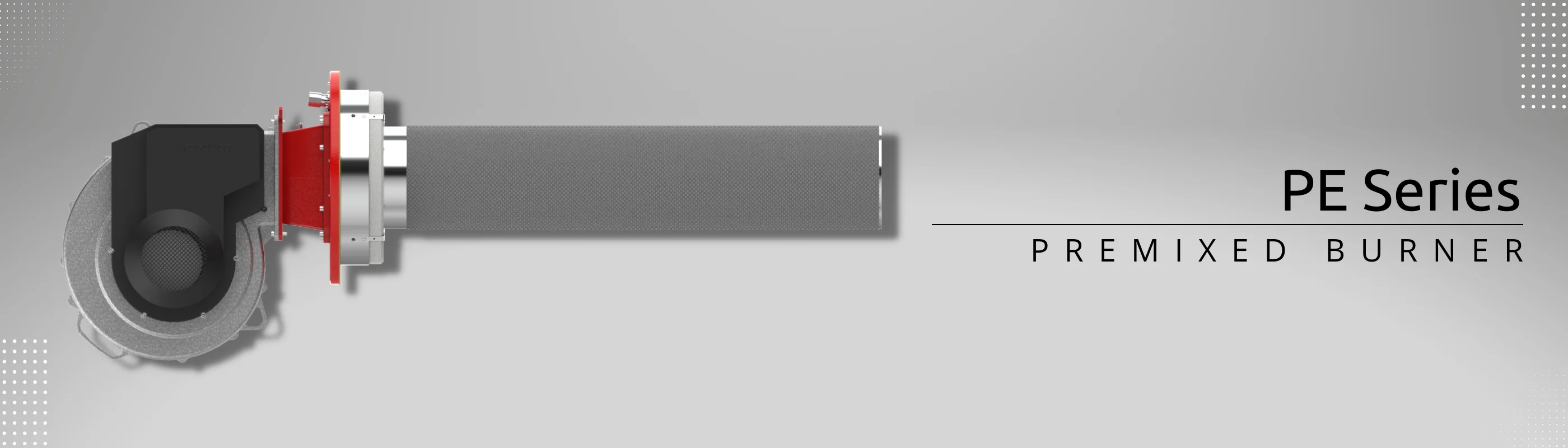
Premixed Burners : burner in which part, or all, of the air for complete combustion of the gas, is mixed with the gas upstream of the mixture outlet ports.
For example, air and gas are thoroughly mixed before the burner head in premixed burners. Then, the mixture goes through high-temperature stain steel, ceramics, and metal fiber heating heads. Because air and gas are mixed thoroughly, the premix burners are categorized as ultra-low NOx burners, and the CO emission value is approximately zero. Thus, they are widely adopted in residential and commercial utilizations.
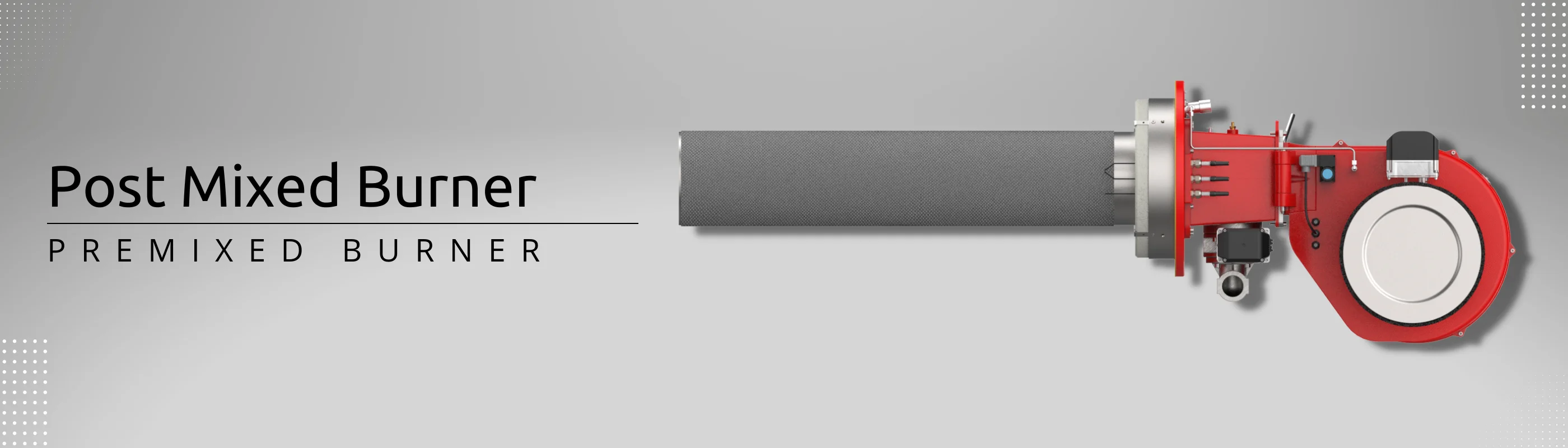
The mixing process can occur before the burner’s fan in a venturi device called premixed burners or PE Series or after the burner’s fan by a cascading twisting mixing device, named post-mixed burners or PM Series. Since the mixed bulk is potentially explosive, using explosion-proof fans (or ventilators) is mandatory in premixed burners.
In «premixed burners», the pneumatic modular system (or pneumatic principle) with Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signal controls the ratio of air/gas mixtures. While, in post-mixed burners, electrical modulating controls can quickly be hired for controlling the burner operation. It is much more straight than an electrical modular burner, using two (or more) independent actuators, has more ability to precisely control the burner, and has many advantages such as 999 points of managing the entire firing range, error monitoring, remote control, valve proving system, etc.
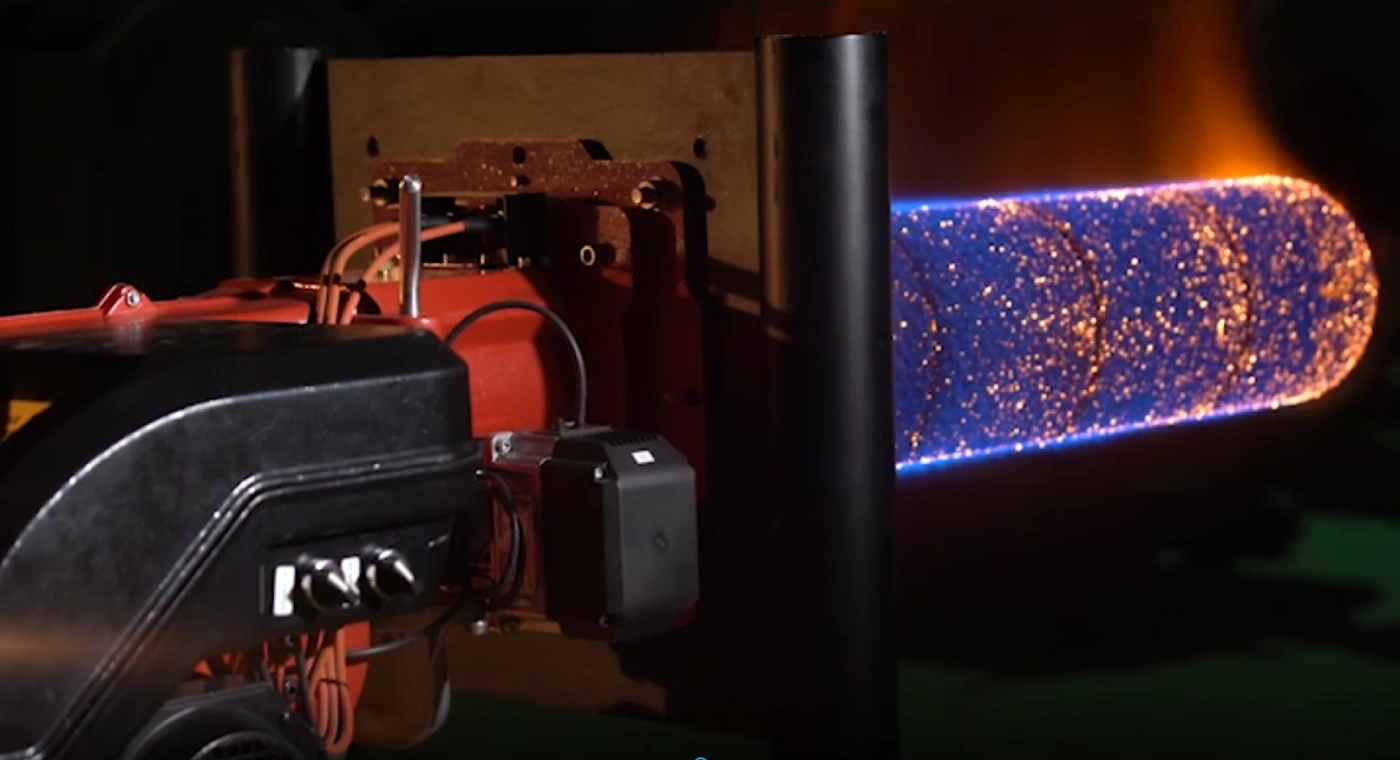



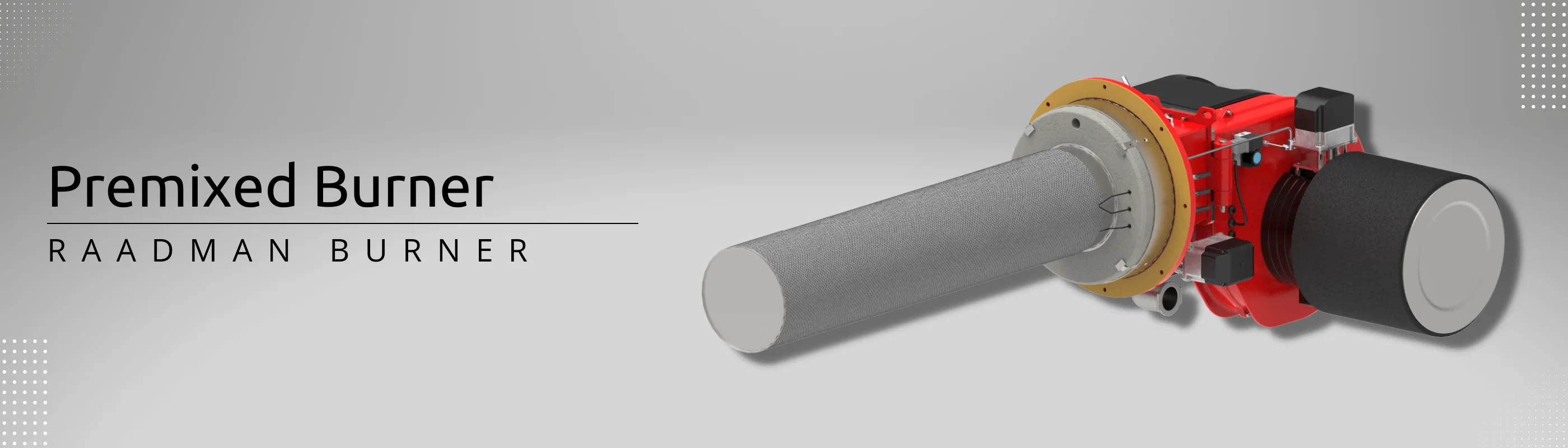









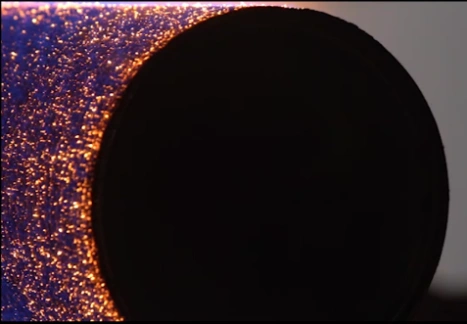 Fiber metal heating head is made of a steel chamber with a coating of metal fibers. Metal fibers are manufactured fibers composed of pure metals and metallic alloys which can be processed into textile products, porous media, plastic-coated metals, etc.
Fiber metal heating head is made of a steel chamber with a coating of metal fibers. Metal fibers are manufactured fibers composed of pure metals and metallic alloys which can be processed into textile products, porous media, plastic-coated metals, etc. Raadman burners have always been particularly efficient and environmentally friendly.
Raadman burners have always been particularly efficient and environmentally friendly. An important feature of these thermal heads is their rapid cooling process, which will occur only a few seconds after the burner is getting turned off during the post-purge period.
An important feature of these thermal heads is their rapid cooling process, which will occur only a few seconds after the burner is getting turned off during the post-purge period.